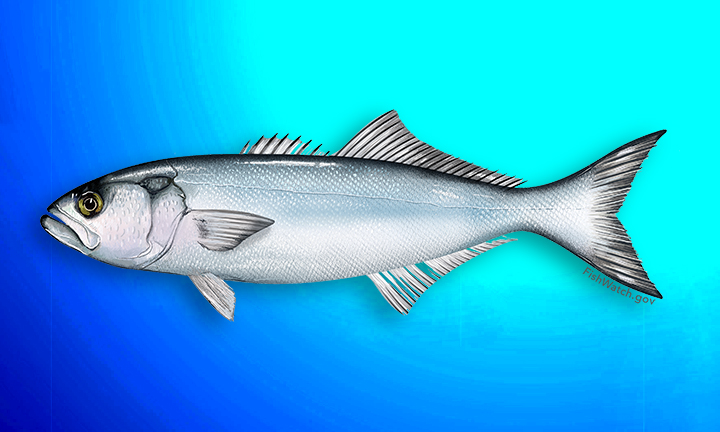
Bluefish
Tailor, Shad, Snapper, Baby blues, Choppers, Elfs, lufar
Bluefish live in temperate and tropical waters around the world with the exception of the eastern Pacific. They are a popular recreational fish along the U.S. Atlantic coast, ranging from eastern Florida to Maine. They can grow to more than 30 pounds (14 kg), gather in large schools and are aggressive feeders.
Bluefish have a bluish green back and silvery sides and underbelly. They have a broad, forked tail, a spiny first dorsal fin, a pointed snout and a prominent jaw, with sharp, compressed teeth. Fillets have a rich, full flavour and coarse, moist texture. Since they prey on small, oil-rich fish, older bluefish tend to have a stronger flavour.
Bluefish are common in pelagic waters on continental shelves around the world. They can be found along the U.S. Atlantic coast, Africa, the Mediterranean and Black Seas, Southeast Asia and Australia. They often migrate from warm to cooler waters in the summer months. In the United States, bluefish are found off Florida in the winter months and by June can be found in New England waters. They mature at two years, when females can lay between 400,000 and 2 million eggs. They spawn in the open ocean, where larvae develop into juveniles and then migrate to estuaries and near-shore habitats. Bluefish can live up to 14 years and grow to more than 30 pounds (14 kg). They are voracious feeders whereby large schools attack forage fish near the surface, churning the water in what is called a “bluefish blitz.” They feed on squid, menhaden and other small forage fish.